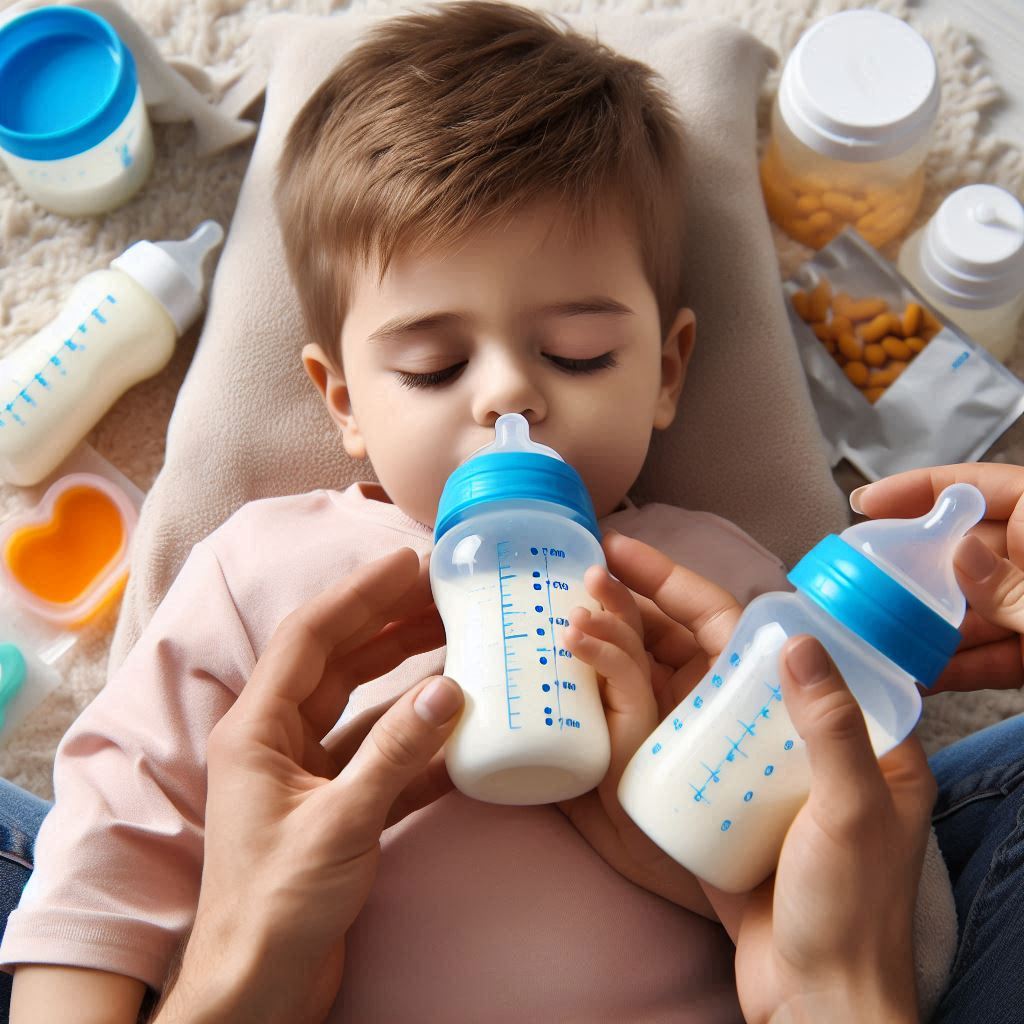
Breastmilk or Formula? Making the Right Choice for Your Baby!
The choice between breastfeeding and formula feeding is a significant one for new parents, as it impacts not only a baby’s immediate nutrition but also their long-term health and development. Each option comes with its unique set of benefits, considerations, and challenges. This article explores the nutritional value of breastmilk versus formula, the factors to consider when making your choice, and some practical tips for parents navigating this decision.

The Nutritional Value of Breastmilk
Breastmilk is widely recognized as the gold standard of infant nutrition. It contains an ideal balance of macronutrients and micronutrients tailored specifically for infants, delivering essential nutrients to promote optimal growth and immune support.
- Proteins and Fats: Breastmilk provides easily digestible proteins, such as whey and casein, which are perfectly balanced to support infant digestion. The fats in breastmilk are essential for brain and nerve development, particularly important during the first two years when cognitive growth is rapid.
- Immunity Boosters: Breastmilk is rich in antibodies, particularly immunoglobulin A (IgA), which coats the intestines and protects babies from harmful bacteria and viruses. Colostrum, the first milk produced post-birth, is especially high in these antibodies and also contains white blood cells that help fight infections.
- Adaptability: Breastmilk evolves in response to the baby’s changing needs, from colostrum rich in immunity-boosting compounds to mature milk with balanced nutrients for growth. It even changes composition during a single feeding session to meet both the hydration and calorie needs of a baby.
- Additional Nutrients: Breastmilk provides essential fatty acids like DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and AA (arachidonic acid), which support brain and eye development. It also contains lactoferrin, which enhances iron absorption and inhibits bacterial growth, protecting the infant’s gut health.
The Nutritional Profile of Infant Formula
Infant formula is crafted to resemble the nutrient profile of breastmilk and is carefully regulated to ensure it provides the essential nutrients babies need. While it may lack the immunity factors of breastmilk, formula has made significant advances in providing balanced nutrition.
- Macronutrients and Micronutrients: Most infant formulas offer a similar combination of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, although the proteins are generally derived from cow’s milk or soy. Formulas also provide a wide array of vitamins and minerals, like calcium, iron, and vitamins D, E, and C, ensuring infants receive a comprehensive nutritional foundation.
- Enhanced Ingredients: Many modern formulas are enriched with DHA and AA to support brain development, along with prebiotics and probiotics for gut health. This helps promote healthy digestion and immunity, offering some of the gastrointestinal benefits found in breastmilk.
- Specialty Formulas: For babies with specific dietary needs or health conditions, specialized formulas are available. For example, lactose-free or hydrolyzed protein formulas help manage sensitivities and allergies, while organic and non-GMO formulas cater to parents looking for alternatives to conventional options.
Key Considerations When Choosing Between Breastmilk and Formula
When making the choice between breastfeeding and formula feeding, a few primary factors should be considered. Here are some aspects to weigh:
1. Health and Medical Considerations
For some babies, breastmilk might be more beneficial due to its immunity-boosting properties. However, certain health conditions in mothers (like infections that can be transmitted through breastfeeding) or specific health needs in infants (like lactose intolerance) may make formula a more appropriate choice.
2. Lifestyle and Convenience
Breastfeeding requires time, frequency, and sometimes lifestyle adjustments, particularly in the early months. Formula can offer more flexibility for working parents or those who need to share feeding duties, as it allows other caregivers to help with feeding. However, preparing formula and sterilizing bottles does require some effort.
3. Nutritional Focus
Some parents prefer breastfeeding due to its natural adaptability to a baby’s needs. Others feel comfortable with formula feeding, knowing it offers balanced nutrition. When opting for formula, you can still prioritize organic, additive-free options to ensure quality.
4. Cost
Breastfeeding is often seen as more economical, requiring fewer resources beyond a nutritious maternal diet and occasional breastfeeding supplies. Formula, particularly specialized or organic options, can be a significant financial investment over time.
5. Bonding and Emotional Experience
Breastfeeding fosters closeness and bonding through skin-to-skin contact. However, bottle feeding with formula can also be a bonding experience, especially when caregivers engage and interact during feedings.
Combining Breastfeeding and Formula
Some families find a mixed approach works best for them. This combination feeding offers flexibility, especially when transitioning back to work or managing other life demands. Here’s how you can make combination feeding effective:
- Establish a Routine: Some parents choose to breastfeed during certain parts of the day, such as mornings and evenings, and use formula during other times. This routine helps maintain a bond while ensuring your baby has adequate nutrition.
- Monitor Digestive Health: Babies’ digestive systems are sensitive, so watch for signs of discomfort, constipation, or gassiness as you introduce formula.
- Focus on Consistency in Nutrition: Ensure your baby receives a balanced intake of nutrients. Most babies adapt to combination feeding with ease, but if there are any concerns, consult your pediatrician to adjust the feeding plan.

Practical Tips for Parents Making the Choice
No matter which choice you make, prioritizing your baby’s health and well-being is the main focus. Here are some tips to keep your feeding routine nutritious and effective:
- Stay Informed: Whether breastfeeding or using formula, learn about your baby’s nutritional needs as they grow. Research types of formulas, or look into lactation consulting if you’re breastfeeding.
- Ensure Maternal Nutrition: If you’re breastfeeding, remember that your diet directly impacts milk quality. Eating a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, leafy greens, and hydration is essential. For formula-feeding parents, remember that regular doctor visits help monitor the baby’s growth and nutrient intake.
- Practice Patience: Both breastfeeding and formula-feeding require some trial and error to figure out the best routine for you and your baby. If you’re struggling with breastfeeding, don’t hesitate to seek lactation support.
- Monitor Baby’s Health and Growth: Keep an eye on your baby’s weight, alertness, digestion, and mood. Whether they’re on breastmilk or formula, these indicators can help assess whether their nutritional needs are being met.
- Seek Support: Reach out to healthcare providers, support groups, and other parents to share experiences and gather insights. Feeding a newborn is an adjustment period for everyone involved.
Conclusion: Trust Yourself and Choose What Feels Right
The decision between breastfeeding and formula is a personal one and may even involve a combination of both methods. Trust your instincts, take note of your baby’s cues, and remember that whatever choice you make can be a healthy, nourishing one. Both breastfeeding and formula feeding can provide your baby with the nutrients they need to grow and thrive. Ultimately, the best choice is one that aligns with your family’s health, lifestyle, and well-being, creating a nurturing environment for both you and your baby.