Egg, Nutrition, Health Benefits & Cognition Diet
Eggs are a nutrient-dense food that can play a significant role in a healthy diet, particularly in supporting nutrition, health benefits, and even cognitive function.
Nutritional Profile
- High-Quality Protein: Eggs contain about 6 grams of protein each, providing all essential amino acids.
- Vitamins: Rich in vitamins such as B12, riboflavin, and folate, which are crucial for energy production and cellular function.
- Minerals: Good source of selenium, phosphorus, and iron, supporting various bodily functions.
- Healthy Fats: Contain monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, along with some saturated fat.
Nutritional Profile
- High-Quality Protein: Eggs contain about 6 grams of protein each, providing all essential amino acids.
- Vitamins: Rich in vitamins such as B12, riboflavin, and folate, which are crucial for energy production and cellular function.
- Minerals: Good source of selenium, phosphorus, and iron, supporting various bodily functions.
- Healthy Fats: Contain monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, along with some saturated fat.
Health Benefits

- Heart Health: Despite past concerns about cholesterol, moderate egg consumption may not significantly impact heart disease risk for most people. Eggs can improve HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
- Weight Management: High protein content can increase satiety, helping to control hunger and reduce overall calorie intake.
- Eye Health: Eggs are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that help protect against age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
- Bone Health: Provide vitamin D and phosphorus, essential for maintaining healthy bones.
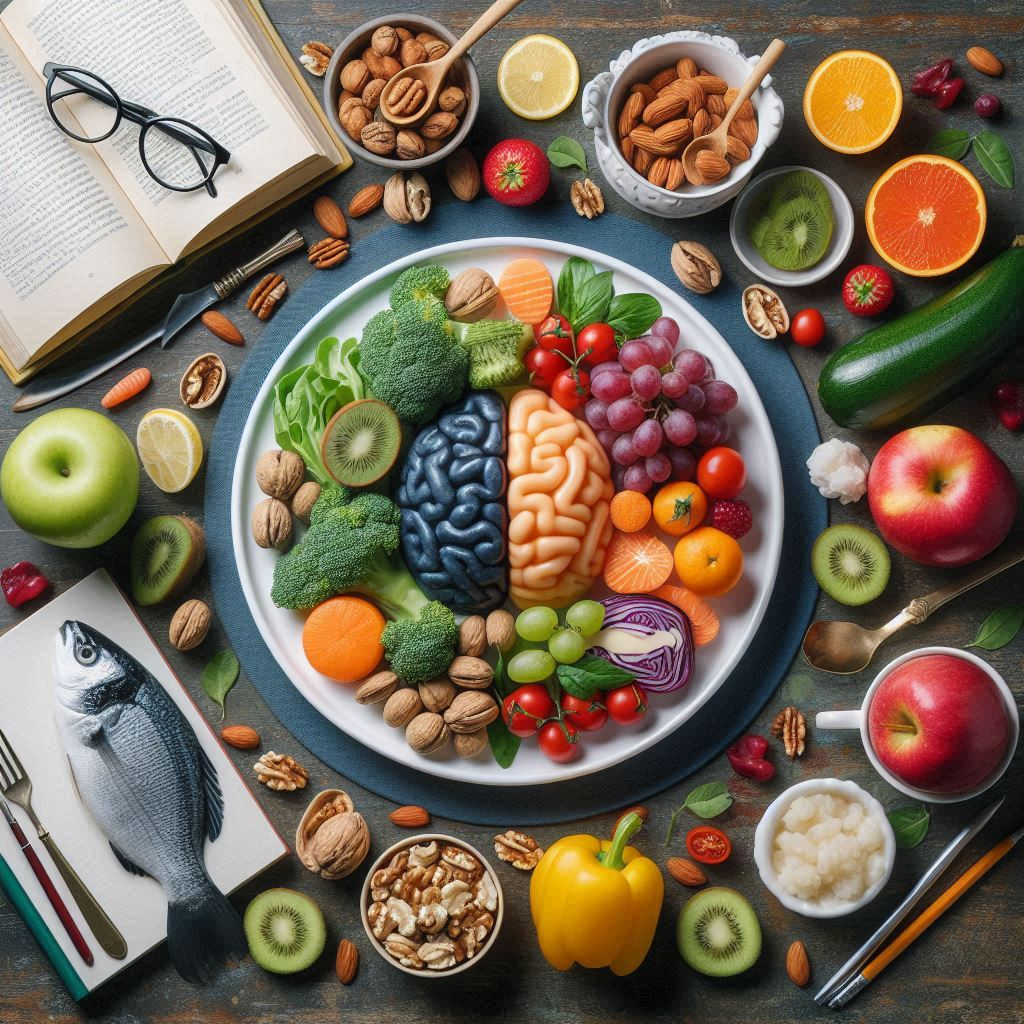
Cognitive Function
- Choline: Eggs are an excellent source of choline, a nutrient that supports brain health, including memory and cognitive function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Eggs from hens fed omega-3 enriched diets can enhance brain function and mood.

Incorporating Eggs into Your Diet
- Breakfast Options: Scrambled, poached, or boiled eggs can be a great start to your day.
- Salads and Wraps: Add hard-boiled eggs to salads or wraps for a protein boost.
- Baking: Use eggs in baking for added structure and nutrition.
A cognition diet focuses on foods and nutrients that support brain health, enhance memory, and improve overall cognitive function.
Key Nutrients for Cognitive Function
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Sources: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds.
- Benefits: Essential for brain structure and function, linked to improved memory and mood.
- Antioxidants
- Sources: Berries (blueberries, strawberries), dark chocolate, green tea, nuts.
- Benefits: Protect against oxidative stress, which can damage brain cells.
- B Vitamins
- Sources: Leafy greens, whole grains, eggs, legumes.
- Benefits: Support energy production and cognitive function, especially B12 and folate.
- Vitamin E
- Sources: Nuts, seeds, spinach, avocados.
- Benefits: Acts as an antioxidant, may help slow cognitive decline.
- Choline
- Sources: Eggs, liver, soybeans, cauliflower.
- Benefits: Important for memory and cognitive development.
- Polyphenols
- Sources: Dark chocolate, berries, red wine, olive oil.
- Benefits: Promote brain health and may improve cognitive function.
Foods to Include
- Fatty Fish: Incorporate salmon, sardines, and trout at least twice a week.
- Leafy Greens: Add spinach, kale, and broccoli to salads, smoothies, or as side dishes.
- Berries: Snack on fresh berries or add them to yogurt and oatmeal.
- Nuts and Seeds: Use walnuts, almonds, and chia seeds as snacks or toppings.
- Whole Grains: Choose brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain bread for sustained energy.
- Dark Chocolate: Enjoy in moderation for a treat that also provides health benefits.
Lifestyle Tips
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water; dehydration can impair cognitive function.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity, which boosts blood flow to the brain.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep to support memory and learning.