Nutrition, Nutrient, Healthy Diet, Vitamin
Nutrition is the science that studies how food and drink impact health and well-being. It focuses on the interactions between living organisms and the substances they consume for sustenance.
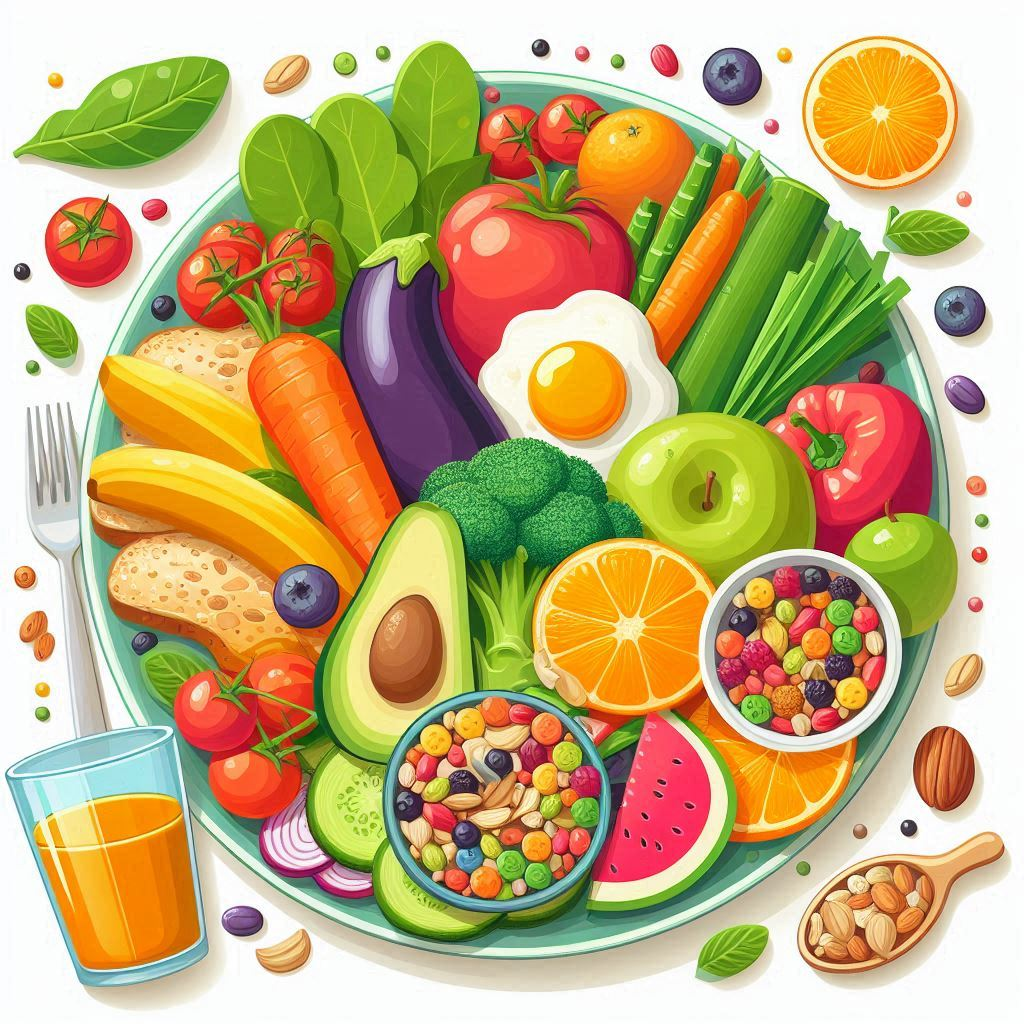
Nutrient Composition: Nutrition examines the composition of foods, including the nutrients they contain—such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals—and how these nutrients contribute to health.

Metabolism: It looks at how the body breaks down and utilizes these nutrients for energy, growth, and repair. This involves processes like digestion, absorption, and metabolism.
Health Impacts: Nutrition explores how different dietary patterns and nutrient intakes influence health outcomes. This includes understanding the role of nutrition in preventing and managing diseases, maintaining optimal body weight, and supporting overall physical and mental well-being.
Dietary Guidelines: Nutrition also includes the development of dietary recommendations and guidelines to help people make healthy food choices. These guidelines are often based on scientific research and aim to promote optimal health and prevent nutritional deficiencies or excesses.
Individual Needs: It recognizes that nutritional needs can vary based on factors such as age, gender, activity level, and health status, and it aims to address these varying needs through personalized dietary advice.
Healthy Diet: A healthy diet is one that helps maintain or improve overall health. It includes a variety of foods in the right proportions and consumption of adequate amounts of food and drink to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. Typically, a healthy diet includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Vitamins: These are organic compounds that are essential in small amounts for various physiological functions. They help the body perform vital processes like energy production, immune function, and tissue repair. Vitamins are categorized into fat-soluble (A, D, E, and K) and water-soluble (C and the B-complex vitamins) groups.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
- Vitamin A
- Role: Supports vision, immune function, skin health, and cell growth. It’s essential for maintaining good vision and immune system function.
- Sources: Liver, dairy products, fish, carrots, and sweet potatoes.
- Vitamin D
- Role: Aids in calcium absorption for bone health, supports immune function, and plays a role in muscle function.
- Sources: Sunlight exposure, fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), fortified dairy products, and eggs.
- Vitamin E
- Role: Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals, and supports immune function.
- Sources: Nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, and green leafy vegetables.
- Vitamin K
- Role: Essential for blood clotting and bone health by aiding in the synthesis of proteins required for blood coagulation and bone metabolism.
- Sources: Green leafy vegetables (like spinach and kale), broccoli, and Brussels sprouts.
Water-Soluble Vitamins

- Vitamin C
- Role: Functions as an antioxidant, supports collagen synthesis for skin and connective tissues, enhances immune function, and aids in iron absorption.
- Sources: Citrus fruits (like oranges and grapefruits), strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
- B-Vitamins
- Role: The B vitamins, including B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12 (cobalamin), are involved in energy production, red blood cell formation, DNA synthesis, and nervous system function.
- Sources: Whole grains, meat, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and leafy greens.
- B1 (Thiamine): Whole grains, pork, legumes, nuts.
- B2 (Riboflavin): Dairy products, eggs, lean meats, green leafy vegetables.
- B3 (Niacin): Poultry, fish, whole grains, nuts.
- B6 (Pyridoxine): Poultry, fish, bananas, chickpeas, potatoes.
- B7 (Biotin): Eggs, nuts, seeds, sweet potatoes, spinach.
- B9 (Folate): Leafy greens, legumes, nuts, seeds, fortified cereals.
- B12 (Cobalamin): Meat, fish, poultry, dairy products, fortified plant-based milk (for those following a vegan diet).