Calcium Supplement, Dietary Supplement, Bone Health, Vitamin D
It sounds like you’re interested in calcium supplements and their relationship with bone health, possibly in conjunction with Vitamin D.

- Calcium: Essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. It’s a key mineral that helps with bone density. Inadequate calcium intake can lead to bone weakening and increase the risk of fractures.
- Vitamin D: Plays a crucial role in calcium absorption in the gut. Without enough Vitamin D, your body can’t absorb calcium effectively, even if you’re consuming it through food or supplements.
- Bone Health: Both calcium and Vitamin D are critical for bone health. Calcium provides the building blocks for bone strength, while Vitamin D ensures that your body can utilize the calcium you take in.
When considering supplements:
- Calcium Supplements: Available in various forms such as calcium carbonate and calcium citrate. Calcium carbonate is best taken with food to enhance its absorption, whereas calcium citrate can be taken with or without food.
- Vitamin D Supplements: Often come in D2 or D3 forms, with D3 being the more effective at raising blood levels of Vitamin D.
Recommended Daily Intake:
The recommended daily calcium intake varies depending on an individual’s age and life stage:
- Infants:
- 0-6 months: 200 mg
- 7-12 months: 260 mg
- Children:
- 1-3 years: 700 mg
- 4-8 years: 1,000 mg
- 9-18 years: 1,300 mg
- Adults:
- 19-50 years: 1,000 mg
- 51-70 years: 1,000 mg for men, 1,200 mg for women.
- 71+ years: 1,200 mg
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women:
- 19-50 years: 1,000 mg
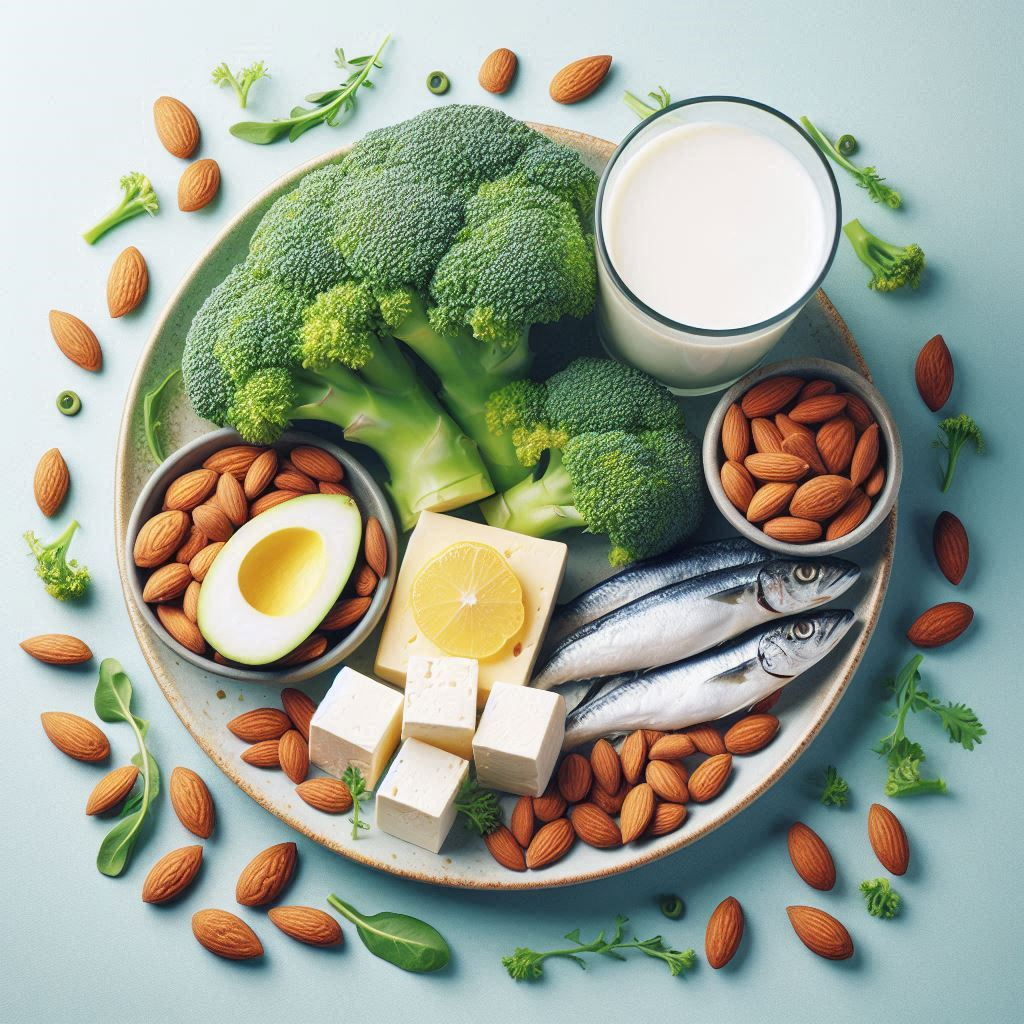
Food Sources of Calcium:
Milk,
Milk products
Fish

Nuts & Seeds
Leafy green vegetables
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin D:
The recommended daily intake for Vitamin D varies by age, life stage, and other factors:
- Infants:
- 0-12 months: 400 IU (10 mcg)
- Children:
- 1-18 years: 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults:
- 19-70 years: 600 IU (15 mcg)
- 71+ years: 800 IU (20 mcg)
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women:
- 600 IU (15 mcg)
Food Sources of Vitamin D
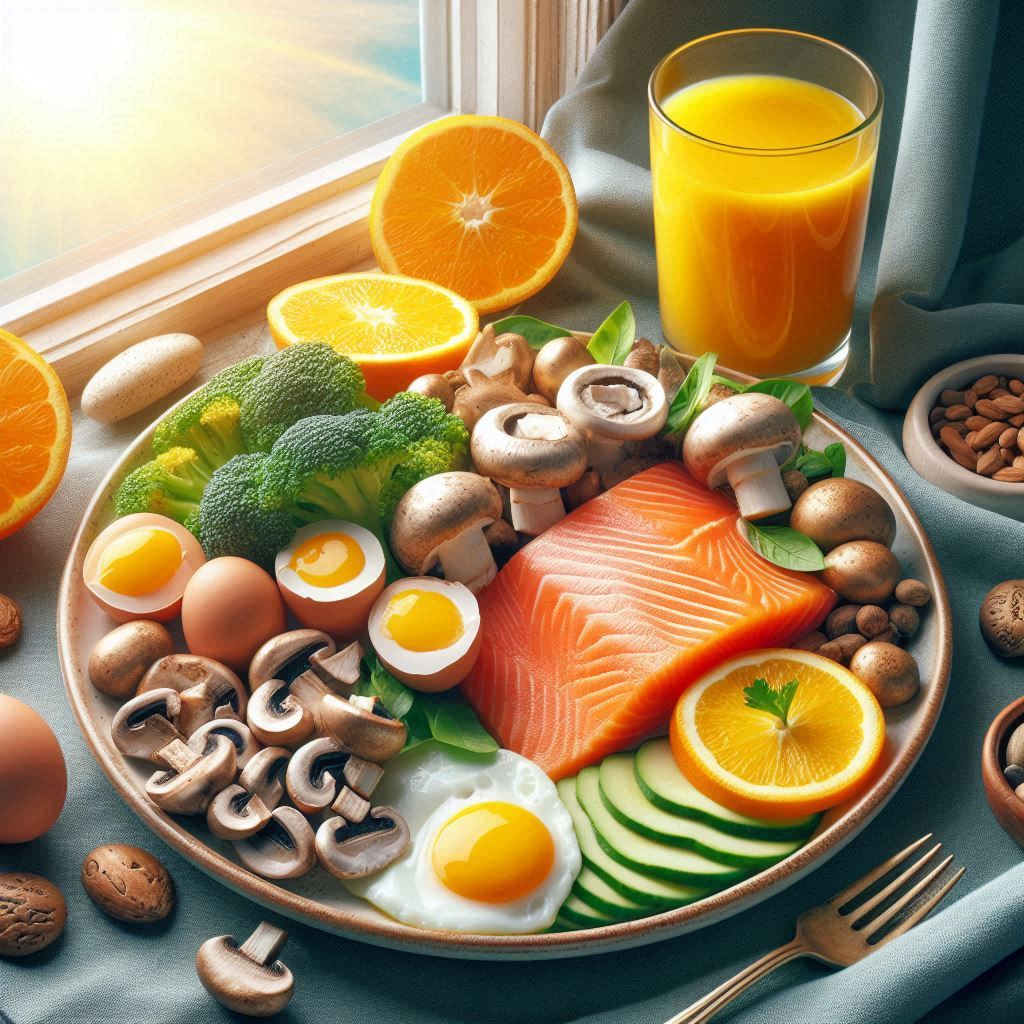

Fatty Fish
Fortified foods
Eggs, cheese
Mushroom,
Cod Liver oil
Notes:
- Vitamin D synthesis by the skin in response to sunlight may reduce the need for dietary intake.
- Many people, especially those with limited sun exposure or specific dietary restrictions, may require supplements to meet their Vitamin D needs.