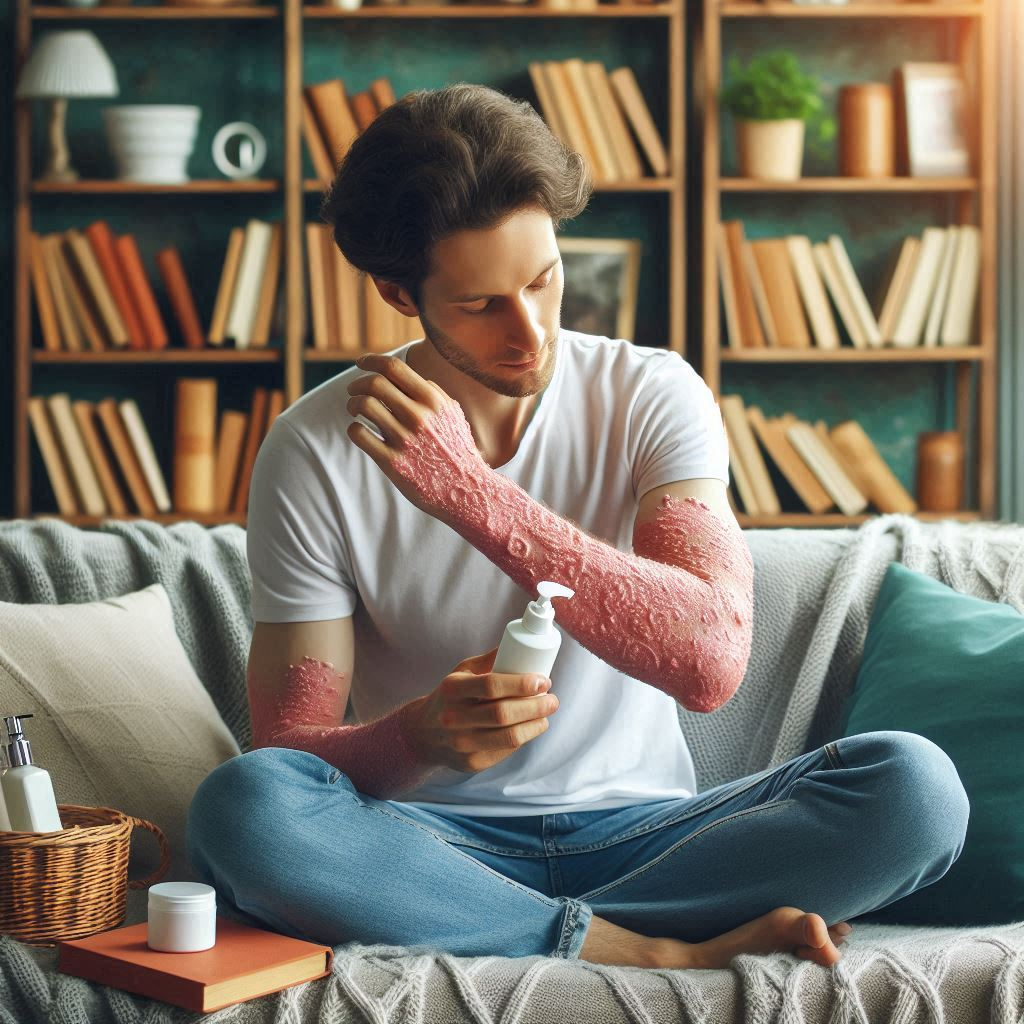
Nutritional Therapy in Persons Suffering From psoriasis
A psoriasis-friendly diet focuses on reducing inflammation and supporting overall skin health. While there’s no one-size-fits-all diet for psoriasis, certain foods and dietary patterns may help manage symptoms.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colorful fruits and veggies. Berries, apples, oranges, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower are particularly beneficial.
- Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Examples include salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds, including almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, are rich in healthy fats and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat can help manage inflammation.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is a good source of monounsaturated fats and antioxidants.
2. Foods to Avoid
- Processed Foods: High in sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives. These can exacerbate inflammation.
- Sugary Foods and Beverages: Excess sugar can lead to inflammation and weight gain, which can worsen psoriasis.
- Red and Processed Meats: These can be pro-inflammatory. Opt for lean proteins instead.
- Gluten: Some people with psoriasis find that gluten aggravates their symptoms, so it might be worth trying a gluten-free diet if you suspect sensitivity.
3. Healthy Lifestyle Tips
- Stay Hydrated: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce inflammation and worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Moderate Alcohol: Alcohol can trigger flare-ups in some people, so it may be helpful to limit your intake.
4. Special Diets

Some individuals find relief by following specific diets like:
- Mediterranean Diet: Mediterranean Diet: Emphasizes fruits, veggies, whole grains, fish, and healthy fats. It’s known for its anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Paleo Diet: Paleo Diet: Focuses on whole, unprocessed foods like meats, fish, fruits, and veggies, while avoiding grains and processed foods.
- Elimination Diet: Involves removing potential trigger foods to see if symptoms improve. Common triggers include dairy, gluten, and nightshades.
Tips for Success
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids (like fatty fish) and healthy fats (like avocado and olive oil).
- Variety: Include a wide range of colorful fruits and vegetables to ensure a good mix of vitamins and antioxidants.
- Moderation: Moderation is key! Limit or avoid processed foods, sugary food, and alcohol to help manage inflammation.