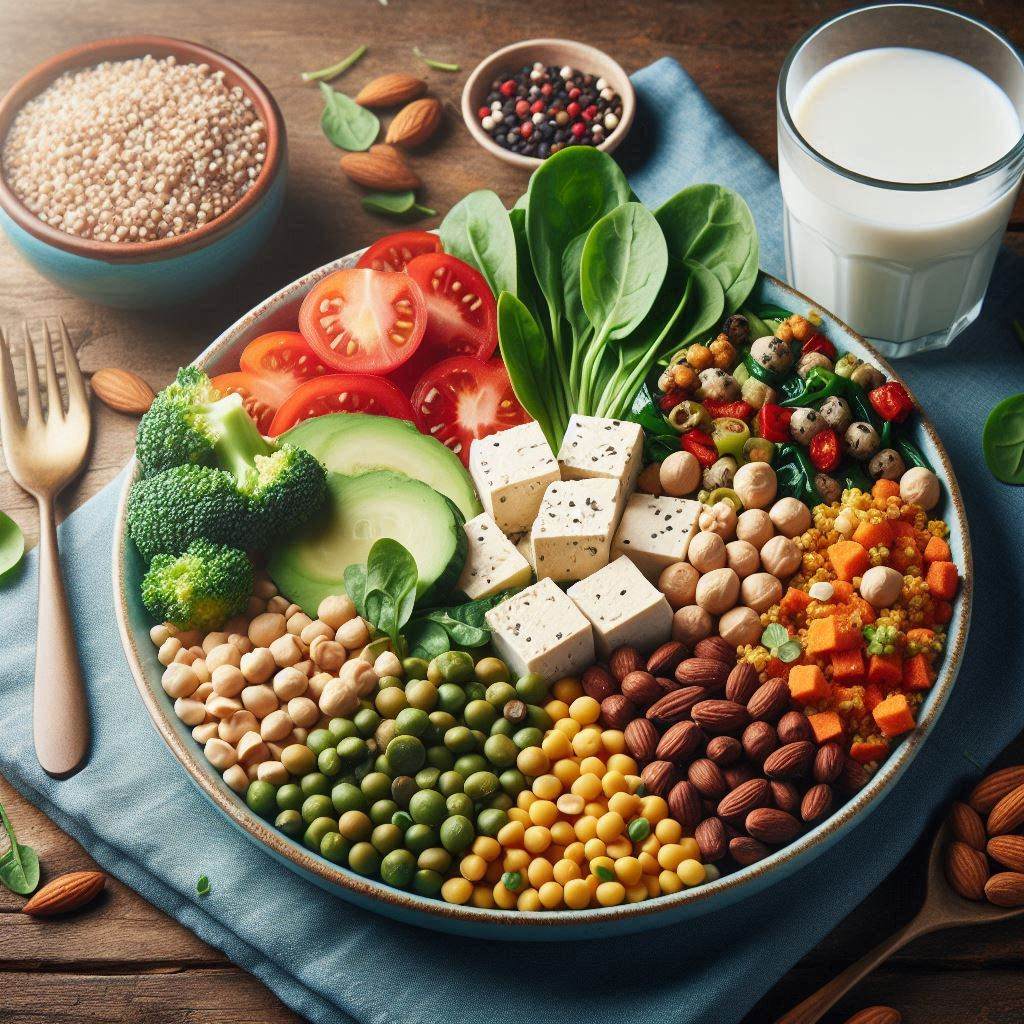
Protein, High Protein diet & Healthy diet nutrition
Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a critical role in the body. It’s made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks for many structures and functions within the body. Here are some key points about protein.
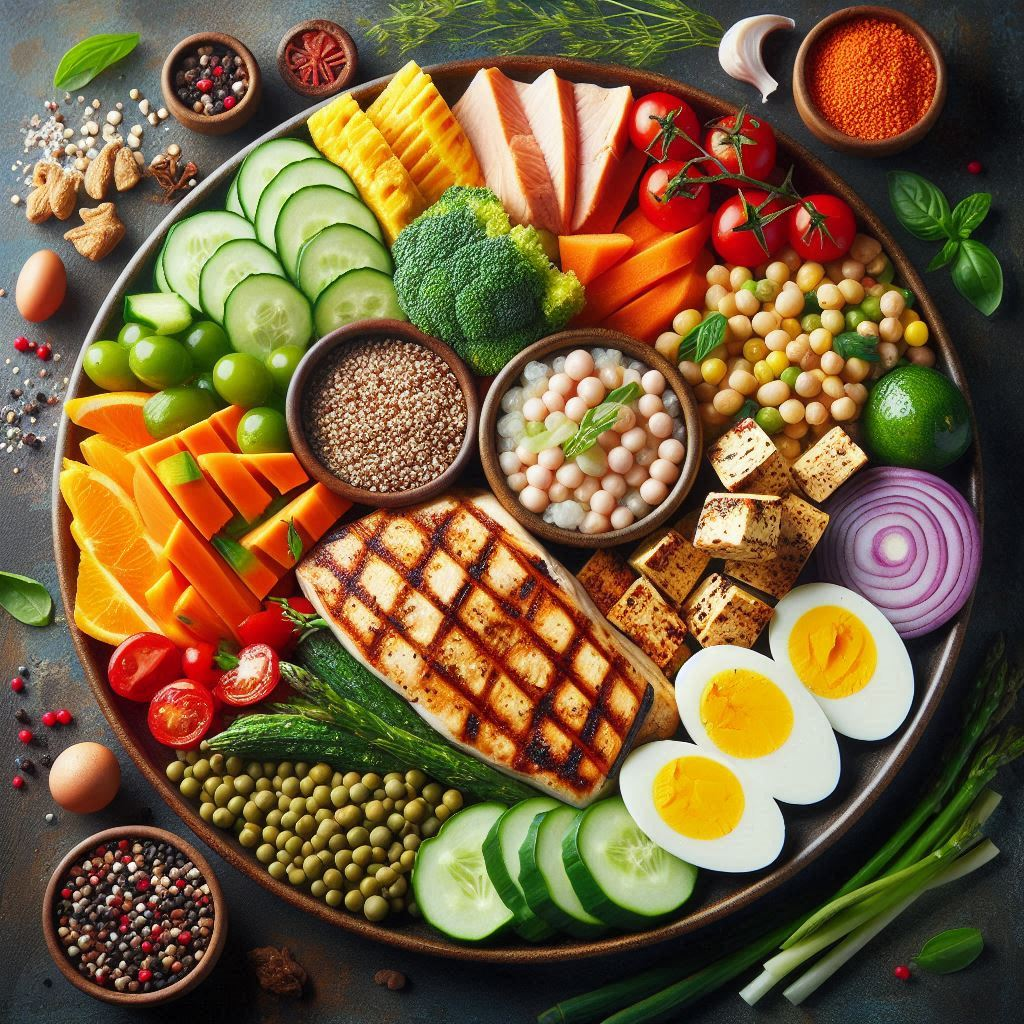

Function: Proteins are involved in nearly every cellular process. They help build and repair tissues, make enzymes and hormones, and support immune function. They are also crucial for muscle growth and repair.
Sources: Proteins can be obtained from both animal and plant sources. Animal-based proteins include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Plant-based proteins can be found in beans, lentils, tofu, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Amino Acids: Proteins are made up of 20 different amino acids. Nine of these are essential, meaning they must be obtained from the diet because the body cannot produce them on its own.
Daily Intake: The amount of protein needed can vary based on age, sex, activity level, and overall health. For many adults, a common recommendation is about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. Athletes or those involved in intense physical activities may require more.
Protein Quality: Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids and are typically found in animal products. Incomplete proteins, which are often plant-based, may lack one or more of the essential amino acids but can be combined (e.g., beans and rice) to form a complete protein profile.
A high-protein diet can be part of a healthy nutrition plan, but it’s important to balance it with other nutrients and consider individual needs. Here’s how you can incorporate a high-protein diet while maintaining overall health:
1. Choose Lean Protein Sources
- Animal-based: Opt for lean meats like chicken breast, turkey, and fish. Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are also good choices due to their omega-3 fatty acids.
- Plant-based: Include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and edamame. Nuts and seeds are also excellent sources.


2. Balance with Other Nutrients
- Carbohydrates: Include whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats) for sustained energy and fiber.
- Fats: Incorporate healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colorful vegetables to ensure a good intake of vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
3. Stay Hydrated
- High-protein diets can increase water needs, so drink plenty of water throughout the day.
4. Portion Control
- Avoid excessive protein intake. Balance your portions to meet your overall caloric and nutritional needs without overloading on protein.
5. Consider Variety
- Rotate your protein sources to ensure you get a wide range of amino acids and nutrients. This also helps prevent dietary monotony.
6. Monitor Your Health
- Regularly check in with a healthcare provider to ensure that a high-protein diet is suitable for you and is not negatively impacting your kidney function or other aspects of health.
7. Meal Planning
- Plan meals to include a source of protein in each one. For example, you could have eggs or Greek yogurt for breakfast, chicken or beans for lunch, and fish or tofu for dinner.
Example Daily Menu for a Balanced High-Protein Diet:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with berries and a sprinkle of nuts or seeds/ Besan chilla + 2egg white
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, avocado, and a vinaigrette/ Paneer rice + 1Bowl mixed dal.
- Snack: A handful of almonds or a protein smoothie with spinach, banana, and protein powder.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli/ Chicken Soup
- Dessert (if desired): Cottage cheese with a bit of fruit/ Milk Shake